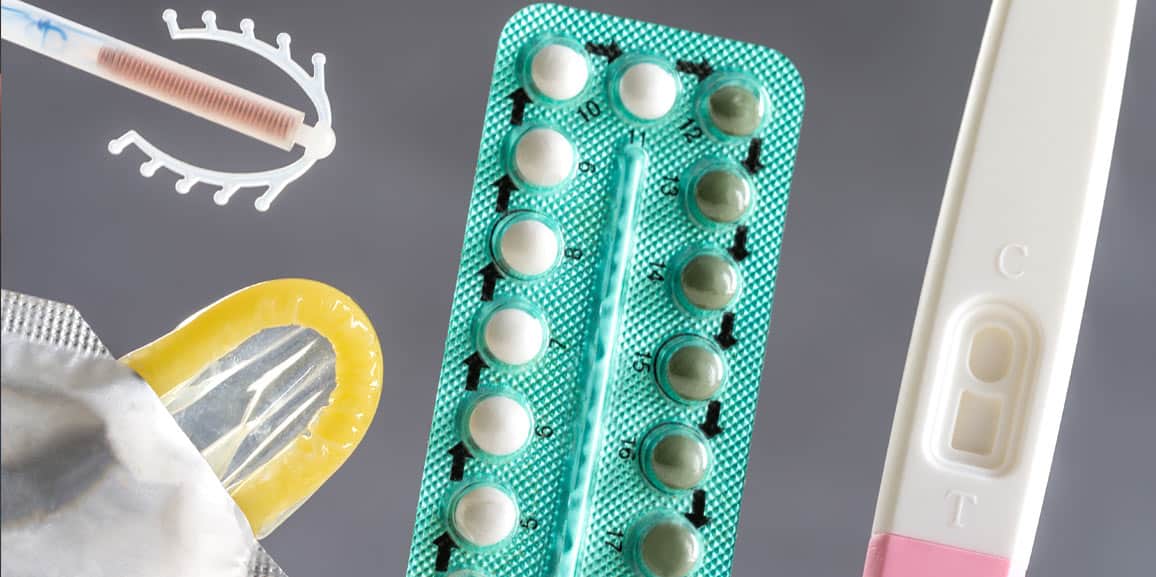
Women today have birth control options . Medical research has produced everything from pills to implants, and research advances every year. Keep reading to discover what options are available!
Hormonal methods
Hormonal birth control refers to any method of birth control where women use hormones like estrogen and progestin to control ovulation. This is a popular method, because it is easily reversible and can involve positive side effects such as reducing menstrual cramps.
Birth control pills
Birth control pills can be very effective when taken correctly. It is most effective when you take your pill at the same time every day (and using a backup method of birth control when you do not take it at that time).
Ring
Contraceptive rings like the NuvaRing is another type of hormonal birth control and is inserted into the vagina. It stays in place for 3 weeks and is removed for week 4. Some women have reported breast tenderness and headaches, while others have noticed a lighter period.
Patch
A birth control patch is another hormonal option, and it is a small patch about 2 inches wide that releases estrogen and progestin. Like the ring, the patch is worn for three weeks then removed for the fourth for your period.
IUD/Implants
Unlike many of the hormonal methods that require a daily pill or regular doctor appointments, an implant or an IUD (intrauterine device) is inserted and can provide continuous birth control for 3-5 years.
An implant is often injected into the arm and can be removed at any time should you wish to try and conceive. The implant releases the hormone progestin that impacts ovulation. Moreover, the hormone helps thicken cervical mucus which blocks sperm.
An IUD is similar but is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. This T-shaped device can be removed at any time, and your doctor will check its placement once a year during your annual checkup.
There are two main types of IUDs: hormonal and copper. The copper IUD is non-hormonal and creates an environment inhospitable for fertilization. The hormonal IUD releases the progestin hormone to control ovulation and thicken the cervical mucus.
Some women may experience some side effects such as breast tenderness, spotting, or heavier periods, but other women may experience positive side effects such as clearer skin and lighter periods, and some women stop having a period altogether.
Barrier methods
The barrier method of contraception is one of the oldest forms of contraception . Barrier methods physically block sperm from fertilizing the egg. You use these contraceptives every time you have sex.
Condoms
The male condom is a tube-shaped barrier that blocks sperm from traveling to the egg. Female condoms fit inside the vaginal canal. Condoms also provide the added benefit of protecting you against sexually transmitted diseases.
Condoms are free at many clinics and are inexpensive and available at many drugstores. Many individuals have noted some loss of sensitivity during intercourse while using condoms.
Diaphragms
A version of the diaphragm has been available to women for decades. It is a soft, flexible disk that physically blocks the cervix. The diaphragm is covered in spermicide and inserted before use.
Diaphragms are not effective against STDs, but they are 88% effective against pregnancy. You need to apply spermicide after each sexual encounter, and the diaphragm must remain in place for six hours after sex.
Some women complain that a diaphragm and spermicide is messy and that using a diaphragm also places you at risk for a urinary tract infection.
Cervical Cap
A cervical cap is placed inside the vagina and filled with spermicide to prevent pregnancy. Like with a diaphragm, the wearer is vulnerable to urinary tract infections, and this method is only 80% effective.
Some people may have an allergic reaction to the spermicide, and many users find this method messy.
Contraceptive sponge
The contraceptive sponge is another barrier-style contraceptive that is 76-80% effective. A sponge soaked in spermicide in inserted into the vagina and left in for six hours after sex. Like other barrier contraceptives, some users find it messy and may have an allergic reaction to the spermicide.
Sterilization
Although most forms of birth control are temporary, there are other options that are permanent.
For women, sterilization may mean tubal ligation (“tube tying”), and for males that might mean a vasectomy. Both of these methods are highly effective. However, there is still a very small chance of pregnancy (vasectomies are 99% effective).
Natural family planning
One option, though statistically the least effective, is to take a natural approach to birth control. That may mean the rhythm method, cervical mucus method, and monitoring basal body temperature.
Most of these methods involve some form of planned abstinence and are often intended to help identify an ideal time to conceive.
Emergency contraceptives
Emergency contraceptive exist as a backup for when your first method of birth control fails or you have unprotected sex. The morning-after pill (e.g., Plan B, Aftera) is a popular emergency contraceptive method.
Side effects
Birth control side effects will vary woman to woman. You may need to try a particular method to see how you feel. Hormonal birth control tends to lead to more side effects, particularly because of the hormonal fluctuations.
For hormonal birth control options , your doctor will likely recommend you try it for three months, then switch to a different pill or a different method if the side effects are too severe.
Contact
The Woman’s Clinic is a Little Rock-based OBGYN that provides flexibility in scheduling, and you will receive the best care from professionals experienced in women’s healthcare.
Contact us at 501-664-4131 to schedule an appointment to discuss your birth control options.